What is a Skin Abscess?
A skin abscess is a painful, swollen lump that forms under the skin and is filled with pus. Pus is a thick fluid composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Abscesses develop when the body’s immune system tries to fight off a bacterial infection that has entered through a break in the skin, such as a cut, or through a hair follicle.
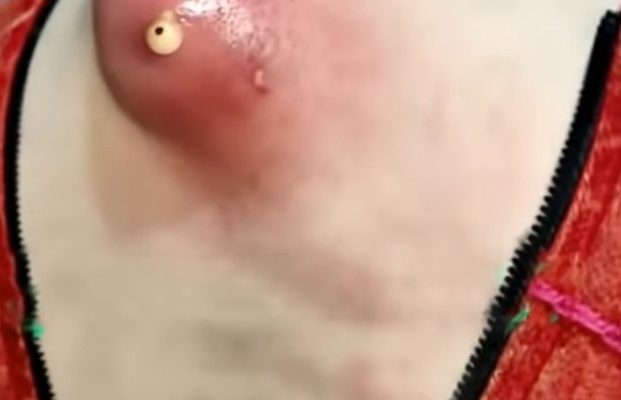
The condition in the image appears to be a particularly large and inflamed abscess, which could be classified as:
- A Furuncle (Boil): An infection that begins in a single hair follicle and the surrounding tissue.
- A Carbuncle: A more severe and deeper infection that is a cluster of interconnected furuncles. Carbuncles are more serious than single boils, as the infection spreads deeper into the skin layers and can lead to a more systemic illness.
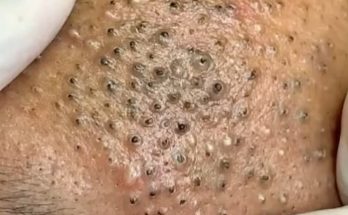
- An Infected Epidermoid Cyst: A pre-existing cyst that has become infected by bacteria, leading to inflammation, pain, and pus formation.
The intense redness, swelling, and prominent “head” (pustule) indicate a mature infection that the body is trying to wall off and expel.
Causes and Risk Factors
The most common culprit behind skin abscesses is the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as “staph.” A particularly dangerous strain is Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which is resistant to many common antibiotics.
Several factors can increase a person’s risk of developing these severe infections:
- A weakened immune system: Conditions like diabetes, cancer, or HIV can make it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Breaks in the skin: Cuts, abrasions, or even insect bites can provide an entry point for bacteria.
- Close contact: Living in crowded conditions or participating in contact sports can increase the spread of staph bacteria.
- Poor hygiene: Not keeping the skin clean can allow bacteria to multiply.
- Pre-existing skin conditions: Eczema or severe acne can damage the skin’s protective barrier.
The Dangers of Self-Treatment
The urge to “pop” or drain such a lesion at home can be strong, but doing so is extremely dangerous for several reasons:
- Spreading the Infection: Squeezing an abscess can force the infected material deeper into the surrounding tissue, causing the infection to spread (a condition called cellulitis). In the worst-case scenario, bacteria can enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis—a life-threatening systemic infection.
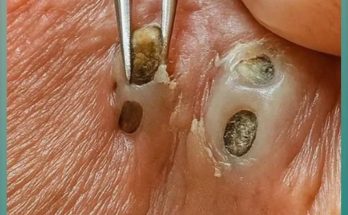
- Incomplete Drainage: Without the proper sterile equipment and technique, it is nearly impossible to drain an abscess completely. Any pus left behind will allow the infection to return, often worse than before.
- Permanent Scarring: Improper handling can cause significant trauma to the skin, resulting in severe and permanent scarring.
- Intense Pain: The procedure is incredibly painful without proper local anesthesia administered by a healthcare professional.
Proper Medical Treatment is Essential
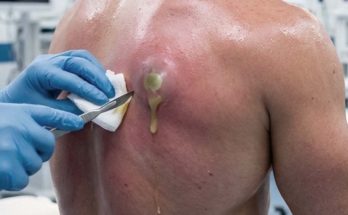
A large, painful abscess like the one pictured requires immediate medical attention. A doctor will typically perform a procedure called Incision and Drainage (I&D).
- The area is first cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic.
- The doctor makes a small, sterile incision to allow the pus to drain out completely.
- A sample of the pus may be sent to a lab to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic.
- The doctor will then clean the empty cavity. In some cases, the cavity is packed with sterile gauze, which helps it continue to drain and heal from the inside out.
- Oral or intravenous antibiotics are often prescribed to eliminate any remaining bacteria and prevent the infection from spreading.
Attempting to treat a severe skin abscess at home is a risk not worth taking. Professional medical intervention is the only safe and effective way to resolve the infection, relieve pain, and prevent serious complications.